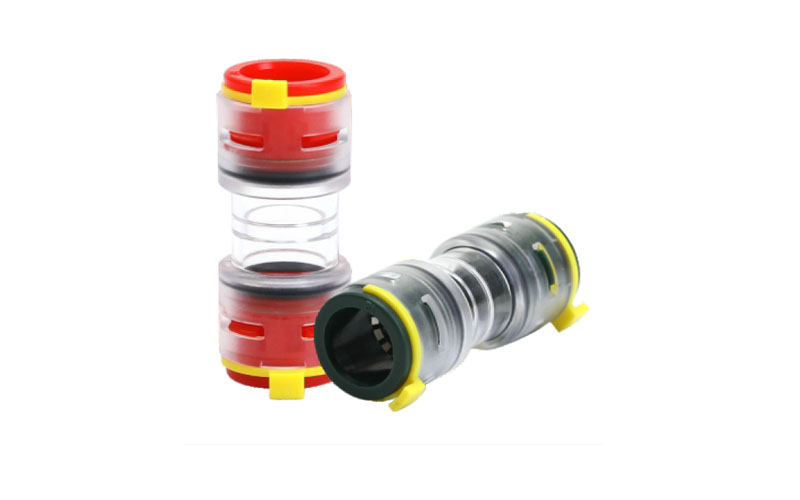

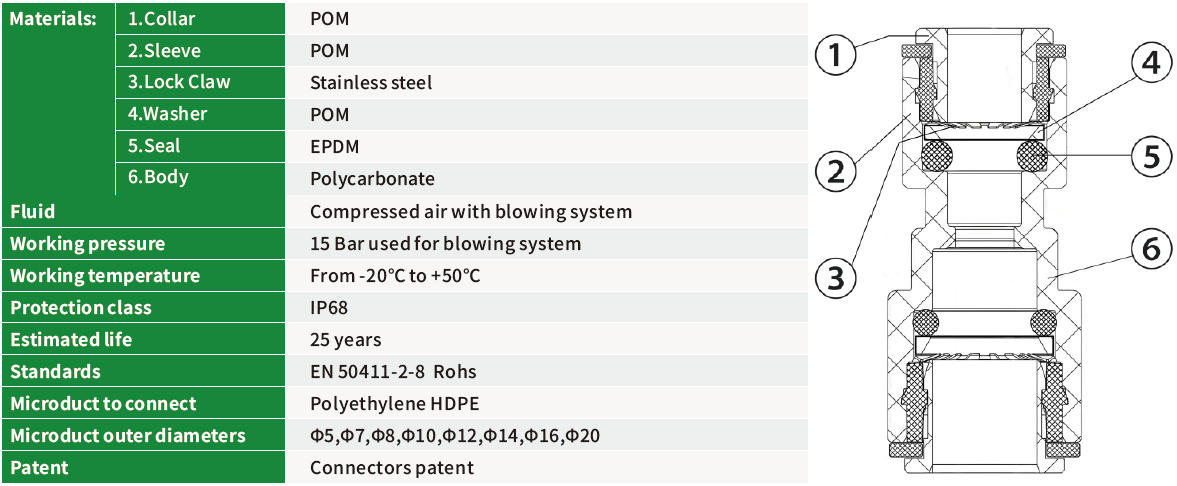
✅ Smooth Transition: It provides a tapered, smooth internal pathway that guides the fiber cable or a smaller microduct (a "sub-duct") from a large diameter to a small diameter without sharp edges or abrupt changes in direction.
✅ Sealing: It often incorporates sealing features (like O-rings or gel seals) to maintain the integrity of the duct system. This is critical for keeping out moisture, dirt, and debris, which can damage the fiber cables.
✅ Mechanical Connection: It creates a strong, secure, and often snap-fit or push-fit connection between the two different-sized microducts, ensuring the network remains physically robust.
✅ Blown Fiber Compatibility: These connectors are essential for networks that use air-blown fiber (ABF) technology. In ABF, cables are installed by being "blown" through the ducts using compressed air. A smooth, sealed transition is vital for maintaining the airflow needed to propel the cable over long distances.
What Problem Does It Solve?
In modern Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) or Fiber-to-the-Premises (FTTP) networks, a main larger duct (e.g., 40mm) is often run through a neighborhood. From this main duct, smaller microducts (e.g., 10mm, 12mm, 14mm) branch off to individual homes or buildings.
The challenge is: How do you protect the fiber cable as it transitions from the spacious main duct into a much narrower pathway without causing friction, damage, or a bottleneck? The Reduction Microduct Connector solves this problem.

© 2024-2026 ARTIC FIBER OPTIC CO.,LTD. All Rights Reserved.