Direct Thermal Tape
How it Works: The printer's heated printhead directly activates a heat-sensitive coating (leucodye) on the label material itself, causing it to turn black.
🔹 No Ink, No Ribbon: This process does not use a separate ink ribbon.
🔹 Image Appearance: The print is matte and can feel slightly waxy.
🔹 Common Use Cases: Shipping labels, receipts, short-term inventory tags, short-duration packaging.
🔹 Pros: Simpler (no ribbon to change), generally lower operational cost.
🔹 Cons:
Not Permanent: The image will fade over time (6-12 months) when exposed to:
✔ Heat (e.g., left in a hot car or warehouse)
✔ UV Light/Sunlight
✔ Abrasion
✔ Chemicals (alcohol, solvents, plasticizers)
✔ Example Materials: Often paper-based, but also synthetic.
Thermal Transfer Tape
How it Works: The printer's heated printhead melts a solid ink from a separate wax or resin ribbon (called a "thermal transfer ribbon") onto the surface of the label material.
🔹 Requires a Ribbon: You must load both the label tape and the compatible ink ribbon.
🔹 Image Appearance: The print is sharp, durable, and can be glossy.
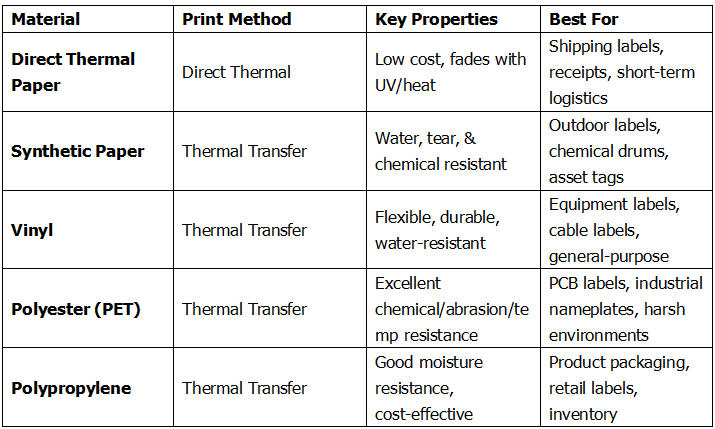
🔹 Common Use Cases: Permanent identification, asset tags, circuit board labels, chemical drum labels, outdoor labels, cable labels, and any application requiring longevity.
🔹 Pros:
✔ Highly Durable: The print is resistant to fading, heat, abrasion, moisture, and chemicals.
✔ Material Flexibility: Can print on a vast range of materials (paper, vinyl, polyester, polypropylene).
✔ Cons: Higher operational cost (requires ribbons), more complex.
✔ Example Materials: Vinyl, Polyester, Polypropylene.
Printer Compatibility: The Most Important Factor
You cannot use any tape in any printer. The choice of tape is dictated by your printer's technology.
✅ Direct Thermal Printers: Can only use Direct Thermal tapes. They do not have a mechanism to hold or use a ribbon.
Examples: Most shipping label printers (Zebra GK420d, Rollo), receipt printers.
✅ Thermal Transfer Printers: Can use both Thermal Transfer tapes AND Direct Thermal tapes (if you simply don't load a ribbon).
*Examples: Brady BMP series, Zebra ZT410, Datamax-O'Neil I-Class.*
✅ Consumer Label Makers: (e.g., Brother P-touch) use proprietary cartridges that contain both the tape and the ribbon (if needed) in a single unit. You generally cannot use loose "roll" tape in these.
Waterproof, oil-proof, tear-proof and scratch-resistant